Quick Overview
FAI is a condition where the bones of the hip joint don’t fit together smoothly, causing painful rubbing or pinching during movement. Over time, this can damage cartilage and lead to arthritis.
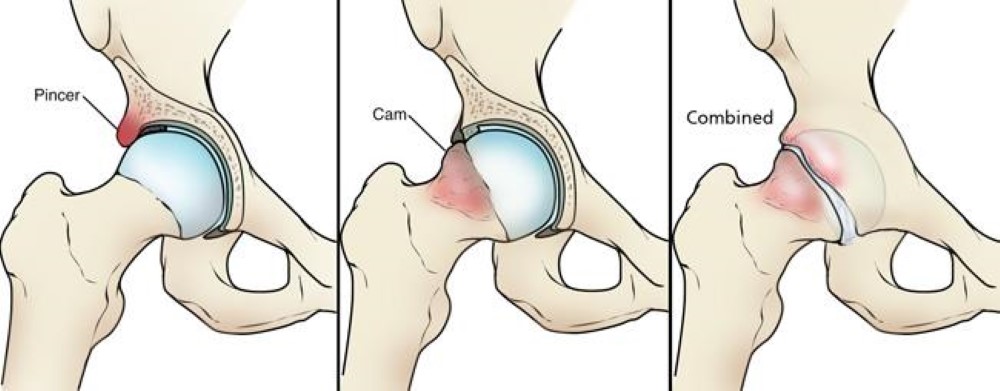
Types of Hip Impingement
There are three main types, based on bone shape:
Cam impingement
Extra bone on the femoral head (top of thigh bone)
More common in males
Pincer impingement
Extra bone on the hip socket
More common in females
Combined impingement
Both cam and pincer present
Common Symptoms
Dull, aching hip pain
Stiffness or reduced range of motion
Limping or difficulty moving
Pain may spread to the groin, buttock, or thigh
Pain worsens with:
Squatting, lunging, jumping
Prolonged sitting
Lying on the affected side
Some people have FAI without symptoms, especially early on.
Causes & Risk Factors
Usually due to abnormal bone shape (often present from birth)
Bone spurs can develop over time
Athletes often notice symptoms sooner due to repeated hip stress
Sports don’t cause FAI, but they can aggravate it
Possible Complications (If Untreated)
Increasing pain and stiffness
Labral tears (damage to hip cartilage)
Higher risk of hip osteoarthritis
Diagnosis
Physiotherapists use:
Physical exam (including specific hip movement tests)
Imaging:
X-rays
MRI
CT scan
Sometimes a diagnostic anesthetic injection to confirm the pain source
Treatment Options
Most people start with non-surgical treatments:
NSAIDs for pain and inflammation
Corticosteroid injections
Physical therapy (strengthens hip muscles, improves movement)
Activity modification (avoid painful motions, not all activity)
Surgery
Considered if symptoms are severe or persistent
Most common: hip arthroscopy
Surgery reshapes the bone and repairs damaged cartilage
High success rate for pain relief and function
Outlook
FAI does not resolve on its own
Symptoms can often be well-managed without surgery
Surgery offers long-term relief for many people
Most patients return to an active lifestyle, sometimes with modified activities
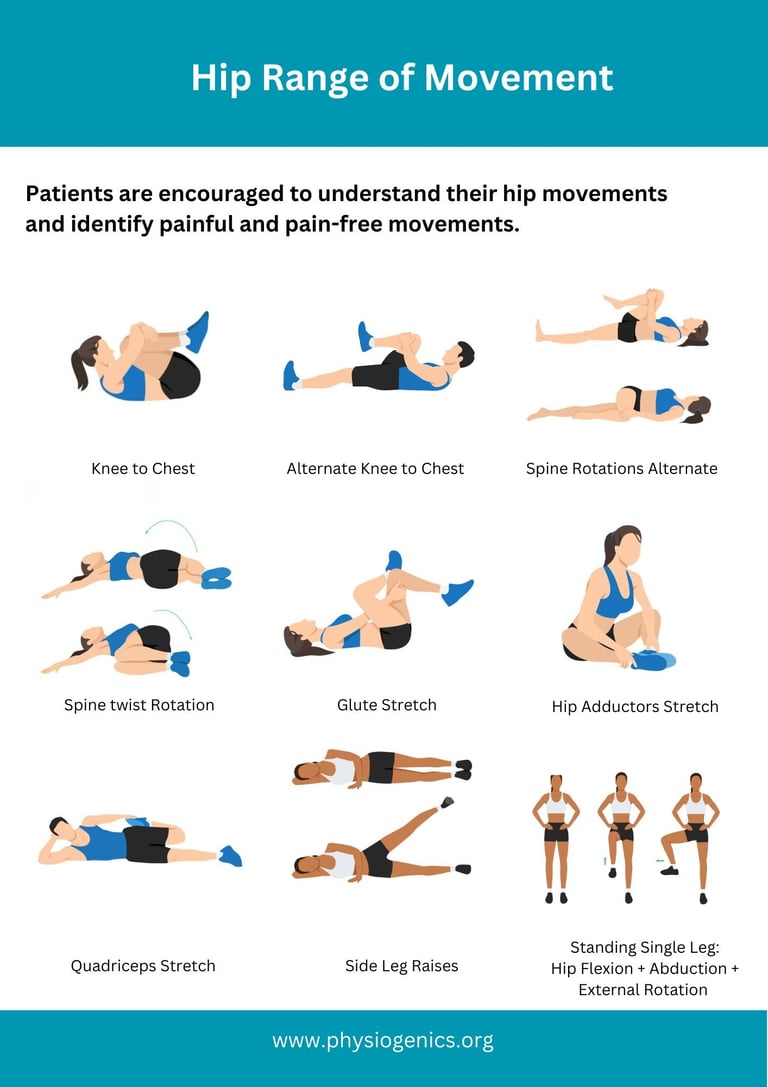
Self Awareness